Making activated carbon from coconut shell involves several steps, including carbonization and activation. Here’s a step-by-step guide:

Steps:
- Collection and Preparation of Coconut Shells:
- Collect coconut shells and clean them thoroughly to remove any residual flesh or fiber.
- Break the shells into smaller pieces to increase the surface area for carbonization.
- Carbonization:
- Place the coconut shell pieces in a large container or drum. Ensure the container can withstand high temperatures.
- Heat the container to around 600-900°C. This can be done by placing the container in a furnace or creating a makeshift kiln.
- Maintain the high temperature for several hours to ensure complete carbonization. This process will turn the coconut shells into char, which is a form of carbon.
- Cooling:
- Allow the container to cool down completely before opening it.
- Carefully remove the charred coconut shells from the container.
4.Activation:
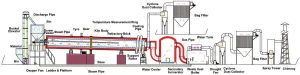
The production method of coconut shell activated carbon can be divided into chemical activation methods and physical activation methods.
Chemical activation is a series of crosslinking or polycondensation reactions between chemical reagents and coconut shell carbonized materials so that the carbonized materials have a rich microporous structure.
Physical activation is to use air, carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other oxidizing gases to react with carbon atoms in the coconut shell carbonized material at high temperatures so that the carbonized material has a rich microporous structure.
The production time of the chemical activation method is short and the required temperature is low. However, the use of a large amount of chemical reagents increases the production cost and has a strong corrosion effect on the equipment, especially in the later stage, a large amount of water is required for washing. These wastewaters can only meet the environmental protection discharge requirements after complex treatment processes. It is for this reason that many people choose to use the physical activation method to produce activated carbon because the process is simple and clean, but the energy consumption is slightly higher.
Physical Activation:
Heat the charred coconut shells to a temperature between 800-1000°C in the presence of steam or carbon dioxide. This helps develop a porous structure.
Chemical Activation (optional but more efficient):
Mix the charred coconut shells with a chemical activator like potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH). A common ratio is 1:3 (activator to char).
Soak the mixture in distilled water for 24 hours.
Dry the mixture at a low temperature to remove excess water.
Heat the dried mixture to around 450-900°C for 1-3 hours. This can be done in a furnace or kiln.
Allow the activated carbon to cool and then wash it with distilled water to remove any residual chemicals.
- Washing and Drying:
Wash the activated carbon several times with distilled water to remove any remaining chemical residues.
Dry the washed activated carbon in an oven at a low temperature (around 110°C) until completely dry.
- Grinding and Sieving:
Grind the activated carbon to the desired particle size.
Sieve the ground activated carbon to achieve uniformity in particle size.
7.Packaging:
After grinding, we will use a packing machine to pack the coconut shell activated carbon into bags, usually 25kg/bag. Then they will be loaded into trucks or stored in warehouses.
8.Applications:

Water treatment: used to remove organic matter, residual chlorine, odor, and heavy metals in water, purifying drinking water, industrial water, and sewage.
Air purification: used to remove harmful gases, volatile organic compounds, and odors from the air.
Food & beverage industry: for the removal of color, odor, and harmful substances.
Medicine & cosmetics: used in the preparation of medicines, oral cleaning products, facial masks, etc., to absorb and remove impurities.
Environmental protection: used for the adsorption and removal of pollutants in soil and water, which is helpful for environmental governance and waste disposal.
Flue gas purification: used for flue gas purification in chimneys and coal-fired industries to remove particulate matter and harmful gases.



